Weight training programs for muscle gain and strength increase: Forget the skinny jeans and embrace the gains! This isn’t your grandpappy’s weightlifting; we’re talking sculpted physiques and Herculean strength, achieved through scientifically-sound programs tailored to your goals. Prepare to embark on a journey of iron-fueled transformation, where sweat becomes your sparkle and muscle is your masterpiece. We’ll unravel the mysteries of hypertrophy, delve into the delicious details of progressive overload, and even throw in a few tips on avoiding the dreaded “noob gains plateau.” Get ready to lift heavier, look better, and feel incredibly awesome.
This guide covers everything from crafting a personalized 12-week beginner program to mastering advanced techniques like progressive overload. We’ll explore the best exercises, perfect your form (because nobody wants a wonky squat), and delve into the crucial role of nutrition and recovery. Think of us as your personal trainers, minus the annoying whistles and overly-enthusiastic high-fives. Let’s get started!
Introduction to Weight Training for Muscle Gain and Strength Increase: Weight Training Programs For Muscle Gain And Strength Increase

So, you want to sculpt yourself into a human Greek statue? Excellent choice! Weight training is your ticket to a stronger, more muscular physique. Forget those flimsy resistance bands – we’re talking serious iron-pumping action here. This isn’t about becoming a bodybuilder overnight (unless you’re secretly a genetically gifted superhuman, in which case, please share your secrets!), but about understanding the science behind building muscle and boosting strength.The fundamental principles behind muscle growth and strength development are surprisingly straightforward, though the execution requires dedication and a touch of strategic genius (or at least a well-planned workout routine).
Essentially, you’re creating microscopic tears in your muscle fibers through resistance training. Your body, being the incredibly clever machine it is, then repairs these tears, making the muscles stronger and slightly larger in the process. This process, known as hypertrophy, is the key to muscle gain. Strength increases, meanwhile, come from improved neural pathways (your brain getting better at telling your muscles what to do) and, of course, increased muscle mass.
Physiological Adaptations to Weight Training
Weight training triggers a cascade of physiological changes. Your muscles aren’t just getting bigger; they’re becoming more efficient. Think of it like upgrading your car’s engine – it’s not just about adding horsepower; it’s about improving fuel efficiency and overall performance. Your bones become denser, reducing the risk of fractures. Your cardiovascular system gets a boost, improving your heart health.
Even your metabolism gets a kick in the pants, helping you burn more calories at rest. It’s a full-body makeover, not just a superficial buff. Imagine a finely tuned machine, operating at peak efficiency – that’s the power of consistent weight training. Studies have consistently shown that regular weight training significantly improves bone mineral density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis, especially in older adults.
For example, a study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research demonstrated a substantial increase in bone density in postmenopausal women who participated in a weight-training program.
Training Methodologies
Now for the fun part: choosing your training style. There are several approaches, each with its own strengths and weaknesses, much like choosing a superhero based on their unique abilities.
Hypertrophy Training
Hypertrophy training focuses on maximizing muscle growth. This typically involves higher repetitions (8-12 reps per set) with moderate weight, ensuring you’re feeling the burn in the target muscle group. Think of this as sculpting your physique with meticulous detail. This approach is ideal for those aiming for a more defined, aesthetic look. An example would be performing 3 sets of 10 bicep curls with a weight that allows you to reach muscle fatigue by the final repetition.
Strength Training
Strength training prioritizes increasing the maximum amount of weight you can lift. This usually involves lower repetitions (1-5 reps per set) with heavier weight. Think powerlifting – moving massive amounts of weight with explosive force. This is perfect for those who want to boost their overall strength and power. A good example would be performing 5 sets of 5 squats with a weight that challenges you to complete all repetitions with good form.
Power Training
Power training combines both strength and speed. It involves explosive movements with moderate weight and focuses on improving the rate of force development. Imagine Olympic weightlifting – those incredibly fast and powerful lifts. This approach is excellent for improving athletic performance and overall explosiveness. An example is performing plyometric exercises like box jumps or medicine ball throws.
Designing a Weight Training Program
So, you’re ready to sculpt your physique like Michelangelo sculpted David (only, hopefully, with fewer questionable anatomical choices)? Fantastic! Designing a weight training program isn’t rocket science, but it does require a bit more planning than just randomly heaving weights around. Think of it as architectural blueprints for your body – you wouldn’t build a house without a plan, would you?Designing a successful weight training program hinges on several key factors: understanding your goals (muscle gain versus strength), your current fitness level, and the principles of progressive overload.
We’ll cover all that, and more, ensuring you’re not just lifting weights, but
strategically* lifting weights.
Beginner 12-Week Muscle Gain Program
This program focuses on building a solid foundation of muscle mass. Remember, proper form is crucial to avoid injuries and maximize results. Don’t sacrifice form for weight! Start light and gradually increase the weight as you get stronger.
| Exercise | Sets | Reps | Rest (seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barbell Squats | 3 | 8-12 | 60-90 |
| Bench Press | 3 | 8-12 | 60-90 |
| Bent-Over Rows | 3 | 8-12 | 60-90 |
| Overhead Press | 3 | 8-12 | 60-90 |
| Dumbbell Bicep Curls | 3 | 10-15 | 45-60 |
| Dumbbell Triceps Extensions | 3 | 10-15 | 45-60 |
Intermediate 16-Week Strength Increase Program
This program is designed for those who have already established a base level of fitness and are looking to increase their strength. We’ll incorporate progressive overload techniques to continually challenge your muscles.
| Exercise | Sets | Reps | Rest (seconds) | Progressive Overload |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barbell Squats | 4 | 5-8 | 120-180 | Increase weight by 2.5-5 lbs every 2 weeks |
| Bench Press | 4 | 5-8 | 120-180 | Increase weight by 2.5-5 lbs every 2 weeks |
| Deadlifts | 1 | 5 | 180-240 | Increase weight by 5-10 lbs every 3 weeks |
| Overhead Press | 3 | 6-10 | 90-120 | Increase weight by 2.5-5 lbs every 2 weeks |
| Pull-ups (or Lat Pulldowns) | 3 | 8-12 | 60-90 | Increase reps by 1-2 every week or add weight to lat pulldowns |
Progressive Overload in Weight Training
Progressive overload is the cornerstone of any successful strength training program. It simply means consistently increasing the demands placed on your muscles over time. This could involve increasing the weight lifted, the number of repetitions, the number of sets, or decreasing rest periods. Without progressive overload, your muscles adapt to the training stimulus and stop growing stronger or bigger.
Think of it like this: if you always lift the same weight, your muscles will eventually say, “Been there, lifted that. Bring on something new!”
Adjusting Training Volume and Intensity
There are several ways to adjust training volume (total amount of work performed) and intensity (how hard you’re working). You can manipulate the number of sets, reps, weight, rest periods, and even the exercises themselves. For example, increasing the weight while decreasing the reps increases intensity, whereas increasing reps while keeping the weight constant increases volume. A common strategy is to employ periodization, cycling through different phases of training with varying volume and intensity.
Get the entire information you require about Best weightlifting schedule for building strength and improving physique on this page.
This prevents plateaus and helps avoid overtraining. For instance, a powerlifting program might prioritize low reps and high weight for a few weeks, then shift to higher reps and moderate weight for hypertrophy (muscle growth). This cyclical approach keeps your muscles guessing and prevents adaptation to a single training stimulus.
Browse the multiple elements of Pertandingan sengit to gain a more broad understanding.
Exercise Selection and Techniques
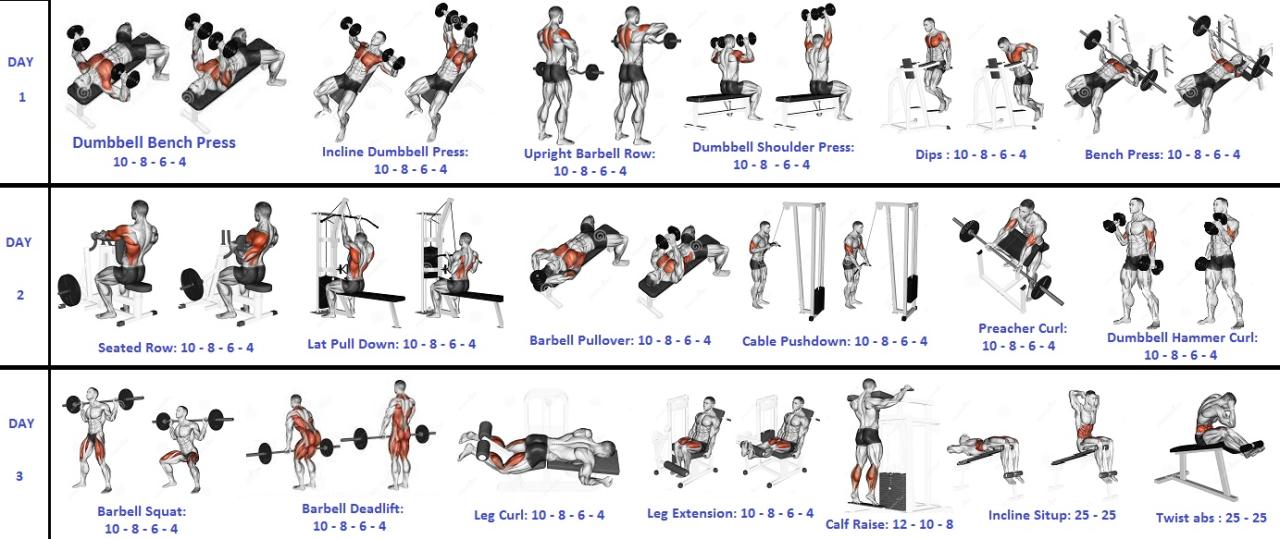
So, you’ve decided to embark on this glorious journey of muscle gain and strength enhancement. Fantastic! But before you start chucking weights around like a caffeinated chimpanzee, let’s talk strategy. Choosing the right exercises and mastering the technique is crucial – otherwise, you risk injury (ouch!) or simply not seeing the results you crave (boo!). This section will arm you with the knowledge to sculpt your physique like a Michelangelo of muscles.
Selecting the right exercises is paramount to maximizing your gains. A balanced program incorporates both compound and isolation exercises, each serving a distinct purpose in your quest for muscle hypertrophy and strength.
Compound and Isolation Exercises, Weight training programs for muscle gain and strength increase
Compound exercises, the heavy hitters of the weight room, work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, leading to significant strength gains and overall muscle growth. Isolation exercises, on the other hand, focus on a single muscle group, allowing for more targeted hypertrophy and addressing specific weaknesses. A smart blend of both is essential for a well-rounded program.
- Compound Exercises (The Big Guns): Squats, Deadlifts, Bench Press, Overhead Press, Bent-Over Rows. These are your foundational movements; they’re like the pillars holding up your strength temple.
- Isolation Exercises (The Detail Work): Bicep Curls, Triceps Extensions, Lateral Raises, Hamstring Curls, Calf Raises. These exercises help refine your physique and address specific muscle groups that might be lagging.
Proper Form and Technique for Key Compound Exercises
Mastering proper form is non-negotiable. Poor form not only reduces effectiveness but also significantly increases your risk of injury. Think of it as learning to drive a Formula 1 car – you wouldn’t want to start by flooring it without proper instruction!
- Squats: Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, toes slightly outward. Lower your hips as if sitting in a chair, keeping your back straight and chest up. Push through your heels to return to the starting position. Imagine you’re sitting on a throne of gains.
- Deadlifts: Stand with feet hip-width apart, the bar over your midfoot. Bend at your hips and knees, keeping your back straight, and grip the bar with an overhand or mixed grip. Lift the bar by extending your hips and knees simultaneously, maintaining a neutral spine. Think of it as picking up a ridiculously heavy prize.
- Bench Press: Lie on a bench with feet flat on the floor. Grip the bar slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Lower the bar to your chest, touching it lightly, and then push it back up to the starting position. Focus on controlled movement, not speed.
- Overhead Press: Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, holding a barbell at shoulder height. Press the bar straight overhead, keeping your elbows slightly in front of your body. Lower the bar slowly back to the starting position. Imagine you’re hoisting a very heavy, very important trophy.
- Bent-Over Rows: Bend at your hips, keeping your back straight, and hold a barbell in front of your thighs. Pull the bar towards your abdomen, squeezing your shoulder blades together. Lower the bar slowly back to the starting position. Think of this as pulling a stubborn donkey (the weight) towards you.
Free Weights Versus Machine Exercises
The age-old debate! Both free weights and machines offer advantages and disadvantages. The best approach often involves a combination of both.
| Feature | Free Weights | Machines |
|---|---|---|
| Muscle Activation | Greater overall muscle activation due to the need for stabilization | More isolated muscle activation, reduced need for stabilization |
| Balance & Coordination | Improves balance and coordination | Less emphasis on balance and coordination |
| Injury Risk | Higher risk of injury if proper form isn’t maintained | Lower risk of injury due to guided movement |
| Versatility | Highly versatile, allowing for a wide range of exercises | Less versatile, limited to the specific exercises the machine allows |
The Role of Accessory Exercises
Accessory exercises, while not as heavy-duty as compound movements, play a vital role in optimizing your gains. They allow you to target specific muscle groups, improve weaknesses, and prevent imbalances. Think of them as the finishing touches on a masterpiece.
Examine how The ultimate guide to resistance training for muscle hypertrophy and strength can boost performance in your area.
For example, if your bench press is lagging, incorporating triceps extensions and incline dumbbell presses as accessory exercises can help address any weaknesses and boost your overall strength.
Nutrition and Recovery for Optimal Results

Building muscle isn’t just about lifting heavy; it’s about fueling your body like a finely-tuned sports car (but, you know, with more protein). Think of your muscles as tiny construction workers: they need the right materials to build and repair themselves after a grueling workout. Ignoring nutrition is like giving them toothpicks and expecting a skyscraper. This section will delve into the crucial role of nutrition and recovery in maximizing your gains.
Macronutrient Intake for Muscle Growth and Recovery
Protein, carbohydrates, and fats—the macronutrient trifecta—are essential for muscle growth and recovery. Protein provides the building blocks (amino acids) for muscle repair and synthesis. Carbohydrates replenish glycogen stores, providing energy for your workouts and preventing muscle breakdown. Fats are crucial for hormone production and overall health, supporting the metabolic processes needed for muscle growth. A balanced intake of all three is vital, not just a protein-only approach.
Think of it like a well-oiled machine; each part plays a critical role. Neglecting any one of these macronutrients hinders optimal performance and recovery.
Sample Meal Plan for Muscle Gain
This sample meal plan targets approximately 2500 calories, with a macronutrient ratio of 40% carbohydrates, 30% protein, and 30% fat. Adjust these numbers based on your individual needs and activity level. Remember, consistency is key!
| Meal | Description | Approximate Calories | Protein (g) | Carbohydrates (g) | Fat (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries, nuts, and protein powder | 500 | 30 | 60 | 15 |
| Lunch | Chicken breast salad with quinoa and avocado | 600 | 45 | 60 | 20 |
| Snack | Greek yogurt with fruit | 200 | 20 | 20 | 5 |
| Dinner | Salmon with brown rice and steamed vegetables | 700 | 50 | 70 | 25 |
| Snack | Casein protein shake | 500 | 50 | 20 | 10 |
Hydration and Sleep for Muscle Growth
Staying adequately hydrated is paramount. Water is involved in nearly every bodily function, including nutrient transport and waste removal. Dehydration can impair muscle function and recovery. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water a day, more if you’re sweating profusely during workouts. Sleep is equally crucial.
During sleep, your body releases growth hormone, which plays a significant role in muscle repair and growth. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Think of sleep as your body’s “muscle-building factory”—it needs sufficient time to operate effectively.
Supplementation: Benefits and Drawbacks
Supplements can be beneficial, but they shouldn’t replace a healthy diet. Creatine, for example, can enhance strength and power output, while protein powder can help you meet your daily protein needs. However, supplements are not magical; they only support your efforts, not replace them. Always consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before starting any supplement regimen.
Over-reliance on supplements without proper diet and training can lead to imbalances and potential health risks. Remember, a well-balanced diet is the cornerstone of muscle growth; supplements are merely supporting players.
Monitoring Progress and Making Adjustments
Ignoring your progress in weight training is like navigating a maze blindfolded – you might stumble upon some gains, but you’ll also likely bump into a lot of frustrating walls. Tracking your progress is crucial for maximizing muscle growth and strength gains, ensuring you’re on the right path, and preventing those dreaded plateaus. Think of it as your personal fitness GPS, guiding you toward your ultimate physique.Regularly monitoring your workouts allows you to identify what’s working and what’s not.
It provides valuable data to inform your future training decisions, preventing you from wasting time on ineffective exercises or training splits. Essentially, you’re turning your body into a finely-tuned machine, with you as the skilled mechanic.
Tracking Progress Metrics
Tracking your progress involves more than just admiring yourself in the mirror (though that’s certainly a perk!). You need concrete data. This includes meticulously recording the weight lifted, the number of repetitions (reps) completed, and the number of sets performed for each exercise. Consider using a workout journal, spreadsheet, or a dedicated fitness app. In addition to these workout metrics, also track changes in your body measurements (like your waist, chest, arms, and thighs) to get a clearer picture of your overall progress.
Remember, progress isn’t just about lifting heavier; it’s about building a stronger, more sculpted physique.
Identifying and Overcoming Training Plateaus
Plateaus are inevitable. They’re those frustrating periods where your progress seems to stall, no matter how hard you train. Identifying a plateau is straightforward: you’re no longer making progress in your lifts, reps, or body measurements despite maintaining consistent effort and a well-structured program. Don’t panic! Plateaus are a sign that your body has adapted to your current training stimulus.
To break through them, you need to shake things up. This might involve increasing the weight you lift, increasing the number of reps or sets, changing your training split, incorporating new exercises, or adjusting the rest periods between sets. Consider focusing on progressive overload – gradually increasing the weight, reps, or sets over time – to constantly challenge your muscles.
For example, if you’ve been consistently bench pressing 100 pounds for 8 reps for several weeks, try increasing the weight to 105 pounds, or aiming for 10 reps at 100 pounds.
Adjusting Training Programs Based on Individual Response
Your training program isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. What works wonders for one person might be completely ineffective for another. That’s why regular monitoring is so crucial. If you notice that a particular exercise isn’t yielding the desired results, don’t hesitate to swap it out for a similar exercise that targets the same muscle group but with a different movement pattern.
For instance, if barbell squats aren’t giving you the leg growth you’re aiming for, try front squats or leg presses. Pay close attention to how your body responds to different exercises and training variables. Are you experiencing more muscle soreness? Are you making progress? Are you injured?
Listen to your body and adjust your program accordingly.
Incorporating Deload Periods
Think of deloading as giving your body a well-deserved vacation from the intensity of weight training. It’s a planned period of reduced training volume and intensity, typically lasting one to two weeks. Deloading helps prevent overtraining, reduces the risk of injury, and allows your body to recover and rebuild, setting the stage for future gains. During a deload, you’ll reduce the weight you lift, the number of sets and reps, or the frequency of your workouts.
For example, if you normally train five days a week, you might reduce it to three days, or you might reduce the weight you lift by 40-50% and perform fewer sets and reps. This allows your muscles and nervous system to recover, preventing burnout and ensuring long-term progress. Deloading isn’t a sign of weakness; it’s a strategic tool for maximizing your long-term gains.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about Designing a strength training program for maximum muscle growth and strength.
Safety and Injury Prevention
Weight training, while incredibly rewarding for building muscle and strength, can also lead to injuries if not approached with caution and respect. Think of your body like a finely tuned sports car – push it too hard without proper maintenance, and you’ll end up in the garage for repairs (or worse!). This section Artikels crucial safety measures to keep you lifting strong and injury-free.
Common Weight Training Injuries and Their Causes
Ignoring proper form and pushing your limits too quickly are the primary culprits behind most weight training injuries. Strained muscles, pulled ligaments, and tendonitis are common complaints. For example, neglecting proper back posture during squats can lead to lower back pain or even herniated discs. Similarly, using excessive weight with poor form during bench presses can result in shoulder impingement or rotator cuff tears.
Overtraining, neglecting rest, and ignoring warning signs from your body also contribute significantly to injury risk.
Proper Warm-up and Cool-down Techniques
A proper warm-up is not just stretching; it’s about preparing your body for the physical demands ahead. Think of it as lubricating your engine before a long drive. Start with 5-10 minutes of light cardio, like jogging or jumping jacks, to increase blood flow. Then, perform dynamic stretches, such as arm circles, leg swings, and torso twists, focusing on the muscle groups you’ll be working.
This increases range of motion and prepares your muscles for the exertion to come. Cool-downs are equally important. They help reduce muscle soreness and prevent stiffness. Spend 5-10 minutes performing static stretches, holding each stretch for 20-30 seconds. This allows your muscles to gradually return to their resting length.
Imagine a rubber band; stretching it suddenly can cause it to snap, while slowly releasing it allows for a smoother transition.
Importance of Using Proper Lifting Techniques
Proper lifting techniques are paramount to injury prevention. This involves maintaining correct posture, using a full range of motion, and controlling the weight throughout the entire exercise. For instance, during a deadlift, maintaining a neutral spine is crucial to avoid back injuries. Visualize a straight line from your head to your heels. Similarly, controlled movements prevent momentum from taking over, reducing the risk of strain or injury.
Learning proper form from a qualified trainer or through reputable resources is an investment in your long-term health and training success.
Strategies for Preventing Overtraining and Burnout
Overtraining is like constantly pushing the accelerator without ever letting up on the brakes. Your body needs rest and recovery to adapt and grow stronger. Implementing a structured training program with adequate rest days is crucial. Listen to your body; persistent fatigue, decreased performance, and persistent muscle soreness are warning signs of overtraining. Incorporating active recovery methods, such as light cardio or yoga, on rest days can aid in recovery.
Prioritizing sleep, hydration, and a balanced diet are equally important for preventing burnout. Remember, consistency and smart training are key, not intensity at all costs.
Summary
So there you have it – your comprehensive guide to transforming your body through the power of weight training. Remember, consistency is key. Don’t expect overnight miracles (unless you’re secretly a superhero). Stick to your program, fuel your body right, and celebrate those hard-earned gains. Embrace the journey, enjoy the process, and remember, the only thing heavier than the weights you lift is the satisfaction of achieving your fitness goals.
Now go forth and conquer those barbells!
